Acer negundo
Taxonomy: Angiospermae, Sapindales, Sapindaceae, Acer
Published: 2016-07-19
Pollen Description
Shape, Size and Aperture
pollen unit: monad, dispersal unit and peculiarities: monad, size (pollen unit): medium-sized (26-50 µm), size of hydrated pollen (LM): -, shortest polar axis in equatorial view (LM): -, longest polar axis in equatorial view (LM): -, shortest diameter in equatorial or polar view (LM): -, longest diameter in equatorial or polar view (LM): -, pollen class: colpate, polarity: isopolar, P/E-ratio: -, shape: spheroidal, outline in polar view: circular, dominant orientation (LM): -, P/E-ratio (dry pollen): prolate, shape (dry pollen): -, outline in polar view (dry pollen): lobate, infoldings (dry pollen): aperture(s) sunken, aperture number: 3, aperture type: colpus, aperture condition: colpate, tricolpate, aperture peculiarities: -
Ornamentation and Structure
LM ornamentation LM: scabrate, nexine: -, sexine: -, SEM ornamentation SEM: rugulate, perforate, suprasculpture SEM: -, TEM tectum: eutectate, infratectum: columellate, foot layer: continuous, endexine: compact-continuous, intine: monolayered, wall peculiarities: -, supratectal element: -
Miscellaneous
pollen coatings: absent, reserves in cytoplasm: starch, lipids, cell number: 2-celled, Ubisch bodies: -
Author(s) of diagnosis: Sam, Saskia; Weber, Martina
Pictures
Picture legend
- flower(s), photographer: Sam, S.
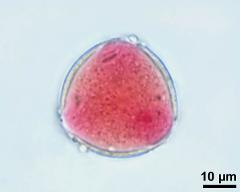
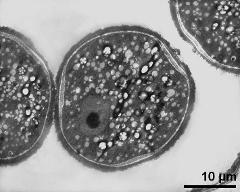
- pollen grain with generative cell - fresh, unfixed, aceto-carmine, photographer: Sam, S.
- upper focus - fresh, acetolyzed, unstained, photographer: Sam, S.
- optical section - fresh, acetolyzed, unstained, photographer: Sam, S.
- lower focus - fresh, acetolyzed, unstained, photographer: Sam, S.
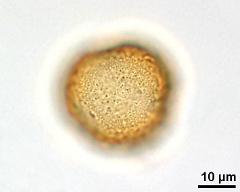
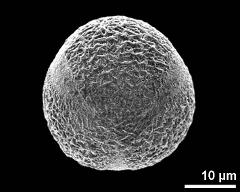
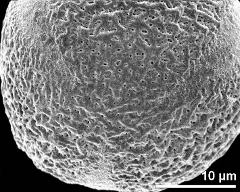
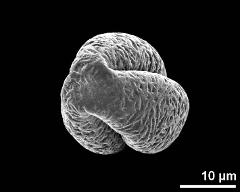
- polar view - fresh, rehydrated (water) & critical point dried & sputter coated with gold, photographer: Sam, S.
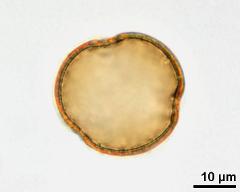
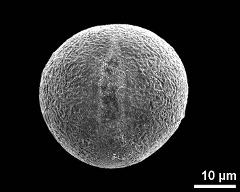
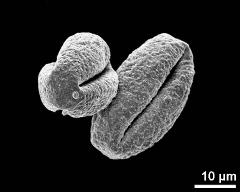
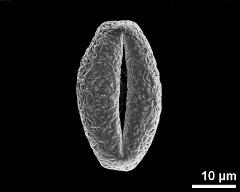
- equatorial view - fresh, rehydrated (water) & critical point dried & sputter coated with gold, photographer: Sam, S.
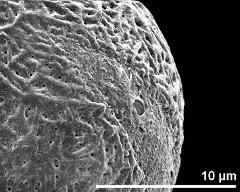
- detail of aperture - fresh, rehydrated (water) & critical point dried & sputter coated with gold, photographer: Sam, S.
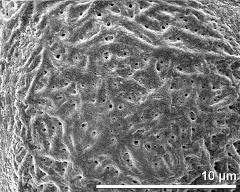
- exine surface - fresh, rehydrated (water) & critical point dried & sputter coated with gold, photographer: Sam, S.
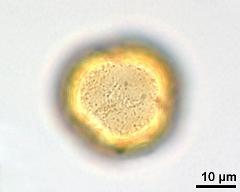
- polar area - fresh, rehydrated (water) & critical point dried & sputter coated with gold, photographer: Sam, S.
- dry pollen grains - dry, sputter coated with gold, photographer: Sam, S.
- polar view (dry pollen grain) - dry, sputter coated with gold, photographer: Sam, S.
- dry pollen grain in equatorial view - dry, sputter coated with gold, photographer: Sam, S.
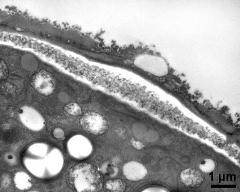
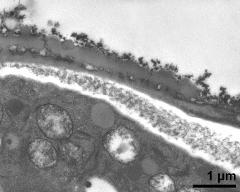
- pollen grain in cross section - fresh, glutaraldehyde & osmium & potassium ferrocyanide, modified Thiéry-test, photographer: Sam, S.
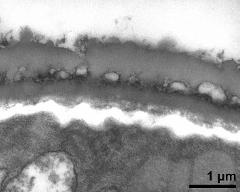
- interapertural area of pollen wall - fresh, glutaraldehyde & osmium & potassium ferrocyanide, modified Thiéry-test, photographer: Sam, S.
- interapertural area of pollen wall - fresh, glutaraldehyde & osmium & potassium ferrocyanide, lipid-test, photographer: Sam, S.
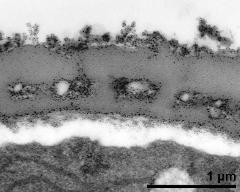
- apertural area of pollen wall - fresh, glutaraldehyde & osmium & potassium ferrocyanide, modified Thiéry-test, photographer: Sam, S.
- pollen wall at transition of aperture and interapertural area - fresh, glutaraldehyde & osmium & potassium ferrocyanide, modified Thiéry-test, photographer: Sam, S.
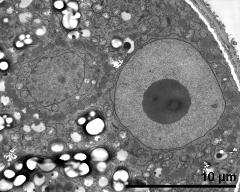
- vegetative nucleus (right) and generative cell (left) - fresh, glutaraldehyde & osmium & potassium ferrocyanide, modified Thiéry-test, photographer: Sam, S.
Literature
- (1990) Morfologia de los granos de polen de las familias Aceraceae, Aquifoliaceae, Geraniaceae, Resedaceae, Sabiaceae y Saxifragaceae del Valle de Mexico. Acta Bot Mex 10: 3-21
- (1976) Pollen morphology of the Aceraceae. Grana 15: 19-27
- (1963) The genera of Sapindales in the southeastern United States. J Arn Arb 44: 462-501
- (1987) Aceraceae, Alismataceae, Amaranthaceae, Apiaceae (Umbelliferae), Araceae, Araliaceae, Cactaceae, Caryophyllaceae, Chenopodiaceae, Droseraceae, Fumariaceae, Lentibulariaceae, Linaceae, Lythraceae, Molluginaceae, Moraceae, Myrtaceae, Oleaceae, Papaveraceae,
- (1978) Aceraceae. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 26: 181-193
- (1976) Flowering and sex expression in Acer. Meded Landbouwhoogeschool 76: 170
- (1963) Pollen morphology in the maples (Acer L.). Pap Michicgan Acad Sci Arts lett 48: 151-162
- (1978) Ultrastruktur und Verteilung des Pollenkitts in der insekten- und windblütigen Gattung Acer (Aceraceae). Pl Syst Evol 131: 277-289
- (1994) Microsporogenesis and endothecial wall patterns in black maple (Acer saccharum subsp. nigrum, Aceraceae). Bull Torrey Bot Club 121: 180-187
- (1991) Gynoecial ontogeny and morphology, and pollen tube pathway in black maple Acer saccharum ssp. nigrum (Aceraceae). Amer J Bot 78: 247-259
- (1981) The pollen morphology of the native New England species of the genus Acer (Aceraceae). Rhodora 83: 237-258
- (1992) The pollen of the genus Acer (Aceraceae) and isomorphism of deviating forms of pollen in dicotyledons. Bot Journ USSR 77: 84-88
- (1993) Polymorphism of pollen in the genus Acer (Aceraceae). Isomorphism of deviate forms of angiosperm pollen. Grana 32: 79-85
- (1972) Blütenökologie und Kultivaren des Spitzahorns (Acer platanoides L.). Acta Musei Silesiae Series Dendrologia 2: 163-170
- (1976) Der Blühverlauf der weiblichen und männlichen Blüten einiger Arten der Gattung Acer L. Acta Musei Silesiae Series Dendrologia 25: 119-128
- (1977) Morphologische Veränderlichkeit und die Blütenökologie der Gattung Acer L. Studie CSAV, Academia Praha : 131
- (1963) The stratigraphical structure of the pollen walls of Dicotyledoneae - I: Ranales and Amentiferae. Acta Phytotax Geobot 19: 137-141
- (1945) Hayfever plants. Waltham Mass, USA
- (1994) Exkursionsflora von Österreich : 1180
- (1998) Preparing living pollen material for scanning electron microscopy using 2,2-dimethoxypropane (DMP) and criticalpoint drying. Biotechnic Histochem 73: 137–143
Copyright and Citation
Cite this publication as:
Sam S., Weber M. 2016. Acer negundo. In: PalDat - A palynological database. https://pc8.botanik.univie.ac.at/pub/Acer_negundo/301248;jsessionid=537CC6610531EE0AFDD6391A6F40D44D; accessed 2025-01-25